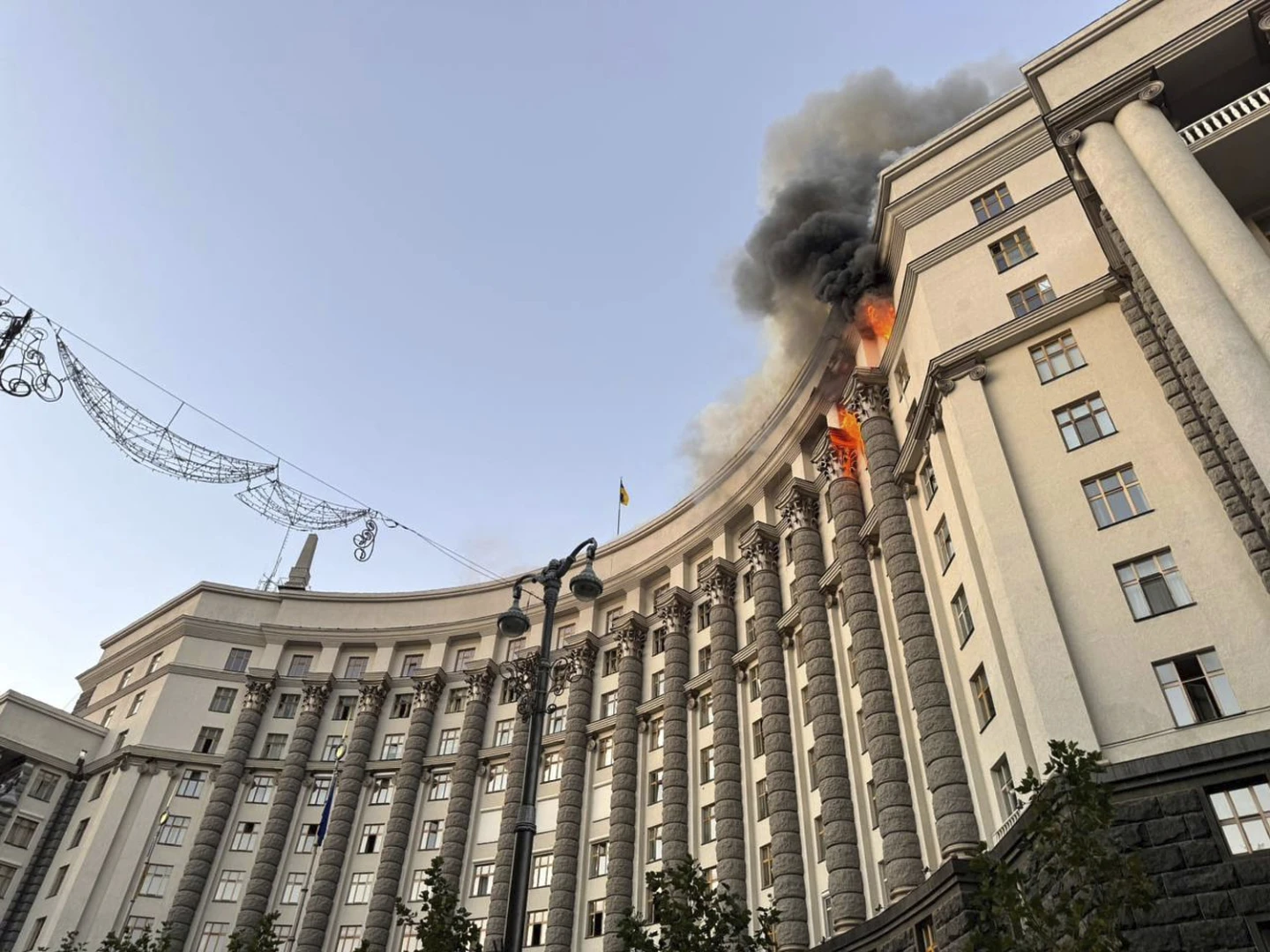
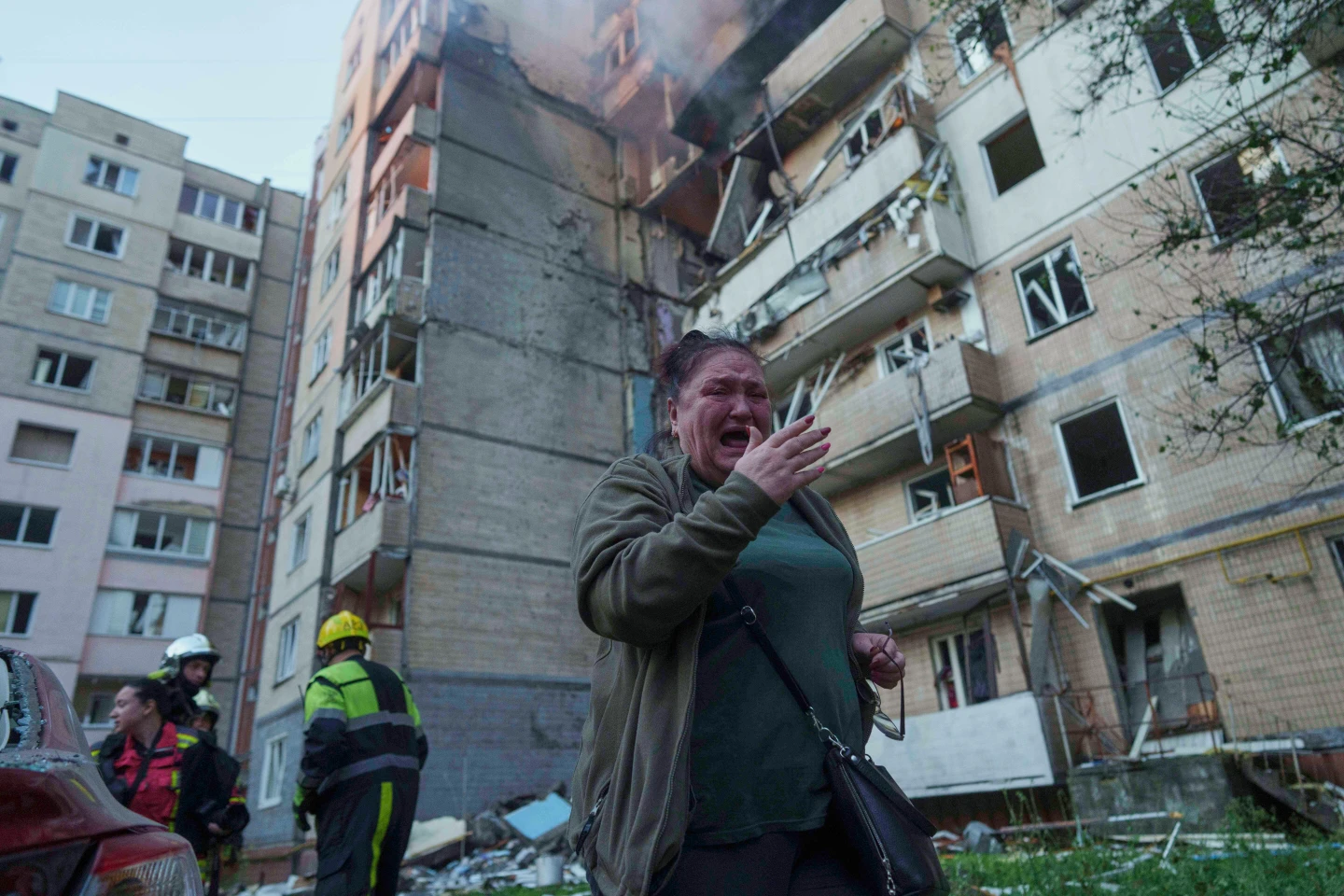
The UK has unveiled a systematic cyber offensive orchestrated by Russian intelligence, which has infiltrated numerous organizations central to foreign aid provision for Ukraine. This assertion came as part of a joint inquiry involving intelligence units from the UK, US, Germany, and France. The NCSC reported that Russian military operatives began hacking public and private entities, aiming to disrupt defense, IT services, and logistics support.
A notable revelation from the NCSC indicates that around 10,000 internet-connected cameras at Ukraine's borders were compromised. These cameras predominantly monitored aid deliveries, including those stationed near military sites and train stations, allowing operatives to monitor material flows into Ukraine. Paul Chichester, Director of Operations at NCSC, highlighted this cyber campaign's implications, stating it poses notable threats to organizations helping Ukraine.
John Hultquist, chief analyst at Google Threat Intelligence Group, alerted that all entities engaged in the transport of goods into Ukraine should regard themselves as potential targets. He also suggested that these cyber endeavors could represent precursor activities leading to more severe actions.
Fancy Bear has employed various hacking strategies to infiltrate critical infrastructure and military supply lines, indicating a potentially broad range of affected entities across 12 European nations and the US. Methods included password guessing and spearphishing, where custom-tailored emails mislead recipients into divulging sensitive information or installing harmful software.
Cybersecurity experts like Rafe Pilling from Sophos noted that tactics utilized by Fancy Bear, including exploiting vulnerabilities in Microsoft Outlook, have been recurrent for over a decade. The implications of camera access extend to tactical advantages for Russian operatives, as it enables them to gauge the flow of materials critical for military logistics.
The cyber-attack narrative serves not just as a reflection of Russia's aggressive espionage strategies but also as an alert to international stakeholders regarding the escalating significance of cyber warfare in contemporary geopolitical conflicts. Experts warn that such attacks might not only aim to gather intelligence but may also disrupt supply chains via both cyber and physical methods, posing increasing risks to nations supporting Ukraine's defense.
A notable revelation from the NCSC indicates that around 10,000 internet-connected cameras at Ukraine's borders were compromised. These cameras predominantly monitored aid deliveries, including those stationed near military sites and train stations, allowing operatives to monitor material flows into Ukraine. Paul Chichester, Director of Operations at NCSC, highlighted this cyber campaign's implications, stating it poses notable threats to organizations helping Ukraine.
John Hultquist, chief analyst at Google Threat Intelligence Group, alerted that all entities engaged in the transport of goods into Ukraine should regard themselves as potential targets. He also suggested that these cyber endeavors could represent precursor activities leading to more severe actions.
Fancy Bear has employed various hacking strategies to infiltrate critical infrastructure and military supply lines, indicating a potentially broad range of affected entities across 12 European nations and the US. Methods included password guessing and spearphishing, where custom-tailored emails mislead recipients into divulging sensitive information or installing harmful software.
Cybersecurity experts like Rafe Pilling from Sophos noted that tactics utilized by Fancy Bear, including exploiting vulnerabilities in Microsoft Outlook, have been recurrent for over a decade. The implications of camera access extend to tactical advantages for Russian operatives, as it enables them to gauge the flow of materials critical for military logistics.
The cyber-attack narrative serves not just as a reflection of Russia's aggressive espionage strategies but also as an alert to international stakeholders regarding the escalating significance of cyber warfare in contemporary geopolitical conflicts. Experts warn that such attacks might not only aim to gather intelligence but may also disrupt supply chains via both cyber and physical methods, posing increasing risks to nations supporting Ukraine's defense.